Version 1
This documentation refers to the version 1.x of the web framework.
The current version of the main branch is documented here.
The Application class¶
The Application class in BlackSheep is responsible of handling the
application life cicle (start, working state, stop), routing, web requests,
exceptions. This page describes details of the Application class:
- How to handle errors.
- Application events and life cycle.
Handling errors¶
BlackSheep catches any unhandled exception that happens during the execution of
request handlers, producing a HTTP 500 Internal Server Error response. To see
this in practice, start an application like the following:
from blacksheep import Application
app = Application()
get = app.router.get
@get("/")
def crash_test():
raise Exception("Crash test")
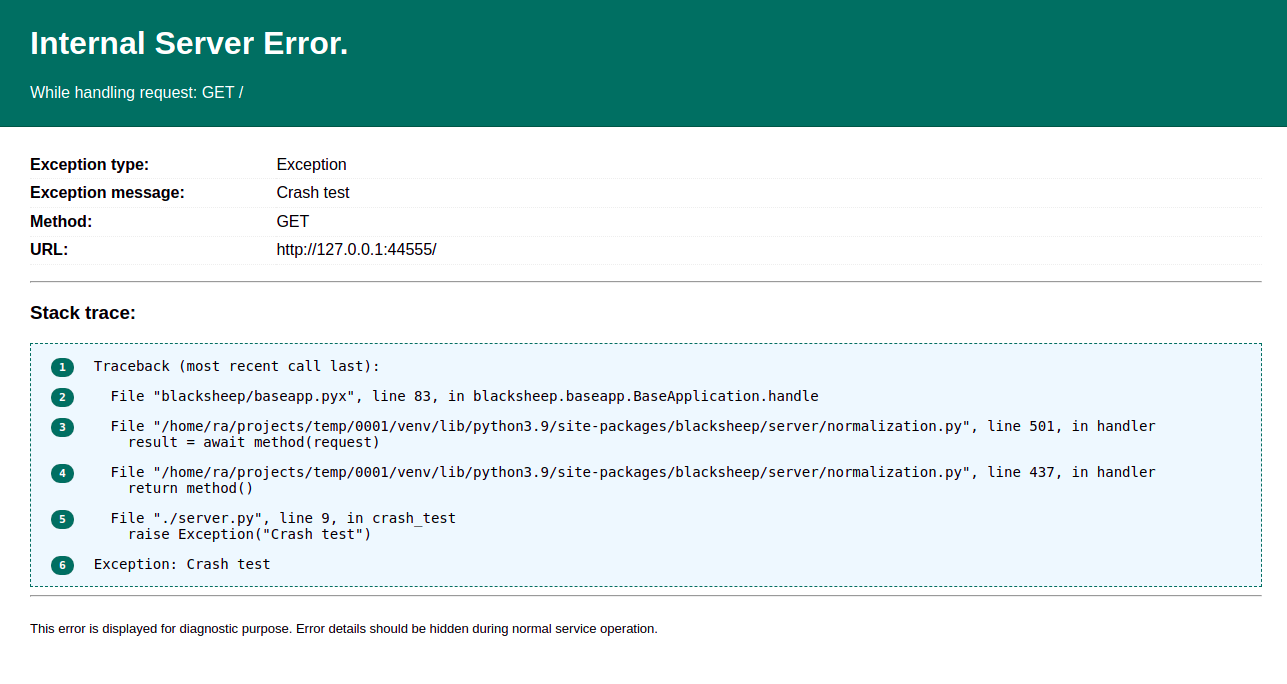
And observe how a request to its root produces a response with HTTP status 500, and the text "Internal server error".
Exception details are hidden to the client by default: it would be a security issue if the web application returned error details to the client. However, while developing and occasionally while investigating issues, it is useful to be able to obtain error details directly from the web requests that are failing. To enable error details, update the app declaration as follows:
app = Application(show_error_details=True)
Now the application returns the details of the exception with the full stack trace, serving a page like the following:
Consider using environmental variables to handle this kind of settings that can vary across environments. For example:
import os
from blacksheep import Application
app = Application(show_error_details=bool(os.environ.get("SHOW_ERROR_DETAILS", None)))
get = app.router.get
@get("/")
def crash_test():
raise Exception("Crash test")
Info
BlackSheep project templates use a library to handle application
settings and configuration roots. Consider using
essentials-configuration
for this.
Configuring exceptions handlers¶
The BlackSheep Application object has a exceptions_handlers dictionary that
defines how errors should be handled. When an exception happens while handling
a web request and reaches the application, the application checks if there is a
matching handler for that kind of exception. An exception handler is defined as
a function with the following signature:
from blacksheep import Request, Response
async def exception_handler(self, request: Request, exc: Exception) -> Response:
pass
In the exception below
class CustomException(Exception):
pass
async def exception_handler(self, request, exc: CustomException):
nonlocal app
assert self is app
assert isinstance(exc, CustomException)
return Response(200, content=TextContent('Called'))
# Register the exception handler for the CustomException type:
app.exceptions_handlers[CustomException] = exception_handler
@app.router.get(b'/')
async def home(request):
# of course, the exception can be risen at any point
# for example in the business logic layer
raise CustomException()
Exceptions inheriting from HTTPException can be mapped to handlers by their type or by
their status code, using int keys; while user defined exceptions are mapped to handlers
by their type.
When an exception handler is registered for a type of exception, all subclasses are also handled by that handler. It is however possible to define a more specific handler for one of the descendant classes.
Configuring exception handlers using decorators¶
It is also possible to register exception handlers using decorators, instead
of interacting with app.exceptions_handlers dictionary:
class CustomException(Exception):
pass
@app.exception_handler(CustomException)
async def handler_example(self, request, exc: CustomException):
...
Overriding the default exception handler for unhandled exceptions¶
To override how unhandled exceptions are handled, define a custom Application
class overriding its handle_internal_server_error method, like in the
following example:
from blacksheep import Application, json
from blacksheep.messages import Request
class MyApp(Application):
async def handle_internal_server_error(self, request: Request, exc: Exception):
# TODO: handle this like you wish!
return json({"message": "Oh, no!"}, 500)
Application events¶
A BlackSheep application exposes three events: on_start, after_start, on_stop. These events can be used to configure callbacks and services that depend on application lifecycle. The application class also offers a useful method to configure objects that need to be initialized when the application starts, and disposed when the application stops: lifespan.
Using the lifespan decorator¶
The Application.lifespan method can be used to register objects bound to the
application life cycle. Common examples of such objects are HTTP clients and
database clients, since they use connection pools that can be initialized
and must be disposed when the application stops.
The following example illustrates how to use the @app.lifespan decorator to
create an HTTP ClientSession that will be disposed when the application
stops. Note how the instance of ClientSession is also bound to application
services, so that it can be injected into request handlers that need it.
import asyncio
from blacksheep import Application
from blacksheep.client.pool import ClientConnectionPools
from blacksheep.client.session import ClientSession
app = Application()
@app.lifespan
async def register_http_client():
async with ClientSession(
pools=ClientConnectionPools(asyncio.get_running_loop())
) as client:
print("HTTP client created and registered as singleton")
app.services.register(ClientSession, instance=client)
yield
print("HTTP client disposed")
@app.router.get("/")
async def home(http_client: ClientSession):
print(http_client)
return {"ok": True, "client_instance_id": id(http_client)}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="127.0.0.1", port=44777, log_level="debug", lifespan="on")
Info
The method leverages contextlib.asynccontextmanager. What is defined
before the yield statement executes when the application starts, and what
is defined after the yield statement executes when the application stops.
The following example illustrates how a redis-py connection can be disposed
using the same method:
import redis.asyncio as redis
...
@app.lifespan
async def configure_redis():
"""
Configure an async Redis client, and dispose its connections when the
application stops.
See:
https://redis.readthedocs.io/en/stable/examples/asyncio_examples.html
"""
connection = redis.Redis()
print(f"Ping successful: {await connection.ping()}")
app.services.register(redis.Redis, instance=connection)
yield connection
print("Disposing the Redis connection pool...")
await connection.close()
Example using Redis
The BlackSheep-Examples repository includes an example where Redis is
used to store access tokens and refresh tokens obtained using
OpenID Connect: example. For more information on redis-py and its async
interface, refer to its official documentation.
on_start¶
This event should be used to configure things such as new request handlers,
and service registered in app.services, such as database connection pools,
HTTP client sessions.
after_start¶
This event should be used to configure things that must happen after request handlers are normalized. At this point, the application router contains information about actual routes handled by the web application, and routes can be inspected. For example, the built-in generation of OpenAPI Documentation generates the API specification file at this point.
on_stop¶
This event should be used to fire callbacks that need to happen when the application is stopped. For example, disposing of services that require disposal, such as database connection pools, HTTP client sessions using connection pools.
Application life cycle¶
Refer to the following diagram to know more about when application events are fired, and the state of the application when they are executed.
How to register event handlers¶
Event handlers can be registered using decorators.
from blacksheep import Application, Request, Response, text
app = Application()
get = app.router.get
@get("/")
async def home(request: Request) -> Response:
return text("Example Async")
@app.on_start
async def before_start(application: Application) -> None:
print("Before start")
@app.after_start
async def after_start(application: Application) -> None:
print("After start")
@app.on_stop
async def on_stop(application: Application) -> None:
print("On stop")
In alternative to decorators, event handlers can be registered using +=:
from blacksheep import Application, Request, Response, text
app = Application()
get = app.router.get
@get("/")
async def home(request: Request) -> Response:
return text("Example Async")
async def before_start(application: Application) -> None:
print("Before start")
async def after_start(application: Application) -> None:
print("After start")
async def on_stop(application: Application) -> None:
print("On stop")
app.on_start += before_start
app.after_start += after_start
app.on_stop += on_stop
Info
For example, to define an after_start callback that logs all routes registered
in the application router:
@app.after_start
async def after_start_print_routes(application: Application) -> None:
print(application.router.routes)
Next¶
Read about the details of routing in BlackSheep.
Last modified on: 2023-07-16 08:51:27
